In this article, we will discuss What is hub device in networking? How its work? Basic features of the hub network. Types of Hub and Advantages and Disadvantages of a hub network.
Table of Contents
Hub in Networking
- A hub is a basic networking device that is used to connect multiple devices together on a local network.
- In a hub-based network, all devices connected to the hub share the same bandwidth, and every device has equal access to the network. When a device sends data, the hub broadcasts the data to all the other connected devices.
- For example– if a hub has eight ports, then any input data that arrives on port 1 will be transmitted to all other ports from 2 to 8.
- It works at the Physical layer (layer 1) of the OSI model.
- It is not an intelligent device because it does not have any memory to store device information. If a computer wants to send information to another computer, the hub broadcasts information to all the other computers, connected to the hub, that’s why it is not an intelligent device.
How Hub Works?
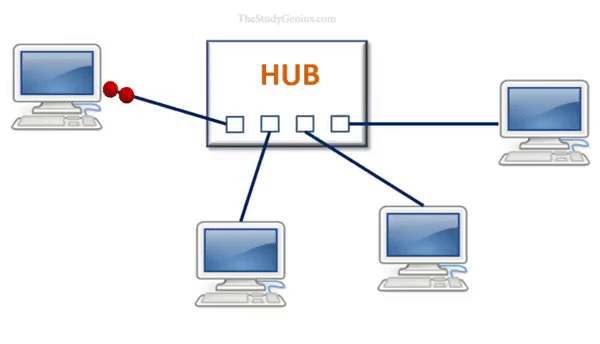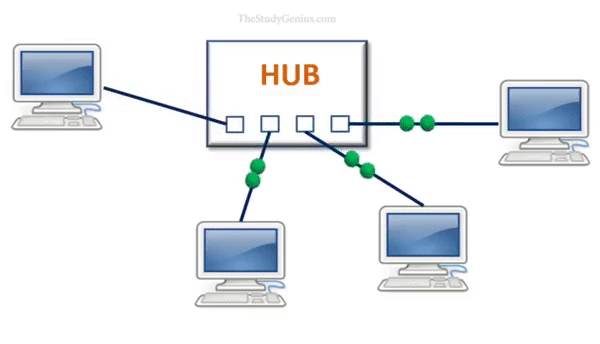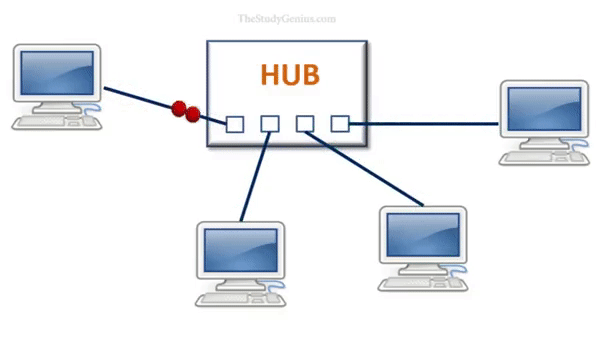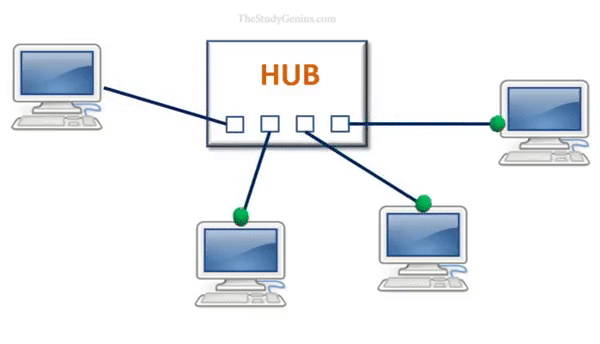
Hub works like an electric wire, it receives data signals from one device in one port and forwards them to all the other ports, except the source port.
The hub does not interpret or process the data in any way. It does not have any capability to identify any frames to know where it should forward because it does not maintain any kind of table like switch. So there is a lot of traffic on the network and network performance is also very poor, only one device transmits information at a particular time.
It works on star topology physically because all the devices are connected to the central node, but logically it acts as a bus topology.
The basic process of a hub device:
- Data transmission: When a device wants to send data to another device on the network, it sends the data to the hub.
- Broadcasting: The hub then broadcasts the data to all other connected devices by transmitting the data out on all of its ports.
- Data reception: The receiving device receives the data from the hub and processes it.
- Data collision: If two devices send data to the hub at the same time, their data will collide and neither device will be able to receive the data.
Basic Features of Hub Network:
- Always Broadcast: Hub always broadcasts the data, whatever computer will connect with the hub, it will broadcast data to all those computers.
- Half-duplex Communication: Hub can communicate only in the half-duplex mode, meaning that data can only flow in one direction at a time. Only one computer can transmit data at a particular time, if other computers want to transmit data, then it has to wait. Other computers can not send data at the same time. If another computer sends data at the same time, the message will collide from both computers.
- Single Collision Domain: Hub works on a single collision domain means two PCs cannot send data at the same time if they send, the packets will collide with each other and the packet destroys. This can lead to decreased network performance and increased network congestion.
- Use only local network: Hub network is used only in the local network means you can use this network in your home or in a small department, etc. This hub network cannot be used in larger networks.
- Cannot store MAC: It is not an intelligent device. It cannot store the MAC address of computers. It does not maintain any kind of table.
- No Data Filtering: Hubs do not filter data, meaning that all data is transmitted to all the connected devices, regardless of its intended recipient.
Why HUB is a physical layer device?
Hub is used in a physical layer because it is not an intelligent device, it does not maintain any kind of table like a switch. It works like a cable (or connector), it’s just simple blindly forwarding data to all the connected devices like a cable. Two devices can not send data at the same time if they try, the packets will collide with each other.
It operates at the lowest level of the networking stack, where the physical transmission of data is managed.
In summary, the hub operates at the Physical layer of the OSI model because it is responsible for the physical transmission of data between devices in a network, without processing or interpreting the data in any way.
You should also read: How Switch Works, How Router Works, How Modem Works, How NIC Works.
Types of Hub in networking
- Active hub
- Passive hub
- Intelligent hub
Active hub needs electricity (AC power) because, it regenerates signals, makes it powerful again, and then sends it forward so it can communicate for long-distance. It acts as a repeater and is also known as a “multi-port repeater”. It can extend communication distance over a network.
Passive hub is simply used to create a network, where it simply receives packets and broadcasts it over the network. It does not amplify signals. It simply receives signals and forwards it.
Intelligent hub, also known as a managed hub or smart hub, provides more advanced features, such as traffic management and remote management capabilities.
Benefits or Advantages of Hub Network
- It can boost the signal which helps to extend the network.
- We can easily create a small network using a hub device.
- It supports different types of network devices.
- It is cheaper than other networking devices, such as switches and routers.
- Provide a centralized connection point for devices in a network, making it easier to manage and maintain the network.
Drawbacks or Disadvantages of Hub Network
- There is no security in a hub network because messages are broadcast to all devices so anyone can access the message.
- It works on half-duplex mode means only one device can communicate at a time.
- It works on a single collision domain if two or more devices try to send data at the same time, the packet collides with each other.
- There is no data retransmission means if the message destroys during transmission for any reason, it will not transmit again.
- It cannot store the MAC address because it does not maintain any kind of table.
You should also read: How Switch Works, How Router Works, How Modem Works, How NIC Works.
Difference Between Hub and Switch | Hub Vs Switch
[table id=3 /]
Video Explanation of Hub Device
You can also Read: